the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License.
the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License.
Going with the floe: tracking CESM Large Ensemble sea ice in the Arctic provides context for ship-based observations
Alice K. DuVivier
Patricia DeRepentigny
Marika M. Holland
Melinda Webster
Jennifer E. Kay
Donald Perovich
In recent decades, Arctic sea ice has shifted toward a younger, thinner, seasonal ice regime. Studying and understanding this “new” Arctic will be the focus of a year-long ship campaign beginning in autumn 2019. Lagrangian tracking of sea ice floes in the Community Earth System Model Large Ensemble (CESM-LE) during representative “perennial” and “seasonal” time periods allows for understanding of the conditions that a floe could experience throughout the calendar year. These model tracks, put into context a single year of observations, provide guidance on how observations can optimally shape model development, and how climate models could be used in future campaign planning. The modeled floe tracks show a range of possible trajectories, though a Transpolar Drift trajectory is most likely. There is also a small but emerging possibility of high-risk tracks, including possible melt of the floe before the end of a calendar year. We find that a Lagrangian approach is essential in order to correctly compare the seasonal cycle of sea ice conditions between point-based observations and a model. Because of high variability in the melt season sea ice conditions, we recommend in situ sampling over a large range of ice conditions for a more complete understanding of how ice type and surface conditions affect the observed processes. We find that sea ice predictability emerges rapidly during the autumn freeze-up and anticipate that process-based observations during this period may help elucidate the processes leading to this change in predictability.
- Article
(6579 KB) - Full-text XML
- BibTeX
- EndNote
In recent decades, sea ice in the Arctic Ocean has undergone rapid change (Serreze and Stroeve, 2015; Stroeve and Notz, 2018). Passive microwave satellite observations since 1979 show that Arctic sea ice extent has decreased in all months, and the 12 lowest September sea ice extents were recorded in the past 12 years (Richter-Menge et al., 2019). The reduced sea ice cover has local effects on boundary layer clouds, temperature, and humidity, which can feedback on the sea ice evolution (Kay and Gettelman, 2009; Boisvert and Stroeve, 2015; Morrison et al., 2019) and the large-scale atmospheric circulation (e.g., Alexander, 2004; Barnes and Screen, 2015; Deser et al., 2016).
Year-round in situ observations are critical for understanding the coupled air–sea–sea ice processes over the remote Arctic Ocean, but they pose enormous challenges. The Surface Heat Budget of the Arctic (SHEBA) project obtained year-round, process-based observations over sea ice when the Canadian Coast Guard icebreaker Des Groseilliers was frozen into the Beaufort Sea and drifted freely with the pack from October 1997 to October 1998 (Uttal et al., 2002). SHEBA observations have been immensely helpful for process-based understanding of the coupled system, and have been widely used to improve modeling of processes in the polar regions (e.g., Intrieri et al., 2002; Bromwich et al., 2009; Klein et al., 2009). Since the late 1990s when SHEBA occurred, there has been year-round sea ice loss (Stroeve and Notz, 2018), there is more first-year sea ice compared to multiyear ice (Maslanik et al., 2011; Nghiem et al., 2007), the pack has thinned substantially (Kwok, 2018; Kwok et al., 2009), and the melt season length has increased (Stammerjohn et al., 2012). Whether or not year-round coupled processes are similar in this new regime of young, thin, seasonal sea ice is an open question.
The international Multidisciplinary drifting Observatory for the Study of Arctic Climate (MOSAiC) experiment has been designed to answer the question: what are the causes and consequences of an evolving and diminished Arctic sea ice cover? MOSAiC aims to assess coupled air–sea–sea ice processes, as well as to investigate the impact on ecosystems and biogeochemistry of the changing system, in order to answer MOSAiC's driving question and improve our understanding and modeling of polar processes in a changing climate (Dethloff et al., 2016). In autumn 2019, the icebreaker RV Polarstern was frozen into the Siberian Arctic with the aim of traversing the Transpolar Drift current over the following year. Extensive analysis using historical satellite data with the IceTrack Lagrangian approach (Krumpen et al., 2019) has been performed in order to identify MOSAiC's starting location, assist with logistical planning, and coordinate research efforts (Krumpen, 2019). Throughout the duration of the experiment, dynamical sea ice forecasts, initialized with and assimilating the most up-to-date ice and weather data, will be performed for the particular MOSAiC track and are available online (https://sidfex.polarprediction.net/, last access: 10 October 2019; coordinated by Helge Goessling). Analyses of an observationally initialized ensemble forecast can provide skillful forecasts for MOSAiC conditions and information about how long these forecasts are skillful before the system diverges from the initial state. These types of in-depth observational and observationally initialized forecast analyses are necessary and important for a successful campaign (IASC, 2016).
In recent years there has been increasing awareness of the impact of internal climate variability on the possible range of sea ice conditions and the resulting representativeness of a single year of observations (Swart et al., 2015; Jahn et al., 2016). In this study, we use data from the Community Earth System Model (CESM) Large Ensemble (CESM-LE) project (Kay et al., 2015). The CESM-LE is an initial condition ensemble, meaning that each ensemble member represents one possible response of the climate system to the external forcing given inherent internal climate variability. The ensemble mean of the individual model experiments represents the response to the changing external forcing, whereas the difference of each ensemble member from to the ensemble mean provides a measure of internal variability. Using the Lagrangian Ice Tracking System (LITS; DeRepentigny et al., 2016), we derive the tracks of virtual sea ice floes for each ensemble member and the evolution of floe conditions over a calendar year. This analysis is not equivalent to examining observational tracks over time. Observational tracks are affected by both internal variability and forced change. Instead, the CESM-LE is an ideal tool for disentangling the effects of internal climate variability from forced change on the conditions a field campaign might encounter.
The purpose of this study is not to provide a forecast for the particular sea ice conditions during MOSAiC. Instead, we use the likely starting condition determined by the MOSAiC planners to address three fundamental goals: (1) offer insight on the representativeness of MOSAiC observations given the range of internal climate variability, (2) provide guidance about what types of observations can best assist with model improvement and appropriate ways these observations can be used to improve climate models; (3) show how free-running climate model simulations might assist with future campaign planning. In Sect. 2, we describe LITS, as well as the CESM-LE and observational data used in this study. Subsequently, Sect. 3 describes the resulting Lagrangian tracks, sea ice conditions along the tracks, and initial-value predictability. We conclude and discuss resulting recommendations for both sea ice observations and models in Sect. 4.
The CESM-LE is a publicly available initial condition ensemble and is designed to assess the role of internal variability in the presence of forced change within the climate system. Each of the 30 CESM-LE members uses an identical code base and external historical and future climate forcing. The ensemble members are unique due to round-off level temperature differences (10−14 K) in the initial atmospheric conditions in 1920. Over time these round-off level differences lead to chaotic evolution in the climate system akin to the initial condition impact on weather forecasts (Lorenz, 1963). Therefore, the spread in individual CESM-LE members is generated solely by internal climate variability. Comparisons between ensemble members allow us to better understand and contextualize the range of possible floe tracks, sea ice conditions, variability, and predictability.
Climate models evolve freely, thus they cannot and should not exactly represent the observed historical Arctic conditions. Therefore, it is neither possible to validate a model by comparing a single climate simulation to the observations nor is it appropriate to directly compare the observations to an ensemble mean, as by design the ensemble mean has damped internal climate variability (Kay et al., 2015). The CESM-LE captures the Arctic sea ice historical state and trends well, and the mean state compares best to the observations relative to other Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Phase 5 (CMIP5) experiments (Barnhart et al., 2015; Jahn et al., 2016). Few other CMIP5 models contribute multiple ensemble members, and none had enough members to adequately quantify the internal variability in Arctic sea ice. In this way, the CESM-LE is unique because it does sufficiently represent the spread in conditions associated with internal climate variability (Jahn et al., 2016). The CESM-LE also reasonably represents the pattern and magnitude of Arctic sea ice thickness (Labe et al., 2018). The CESM-LE sea ice motion patterns are similar to observations, though the Beaufort Gyre circulation is stronger than observed (DeRepentigny et al., 2016). Thus, due to its well-represented Arctic sea ice mean state and variability and the availability of many ensemble members, the CESM-LE is an ideal global climate model for the following analyses.
For this study, 30 CESM-LE members provide daily sea ice concentration and velocity (u and v) fields. We also use satellite-derived sea ice velocity (Tschudi et al., 2016) and concentration (Meier et al., 2017) from 1988 to 2016, for a total of 28 year-long observationally derived drift tracks. We use LITS (DeRepentigny et al., 2016) to track virtual sea ice floes starting from the point 85∘ N, 125∘ E, on 15 October (as provided by Thomas Krumpen, personal communication, 2019, as a likely starting point for the MOSAiC campaign) for (1) satellite-derived historical conditions, (2) perennial Arctic model conditions, and (3) seasonal Arctic model conditions. We obtained simulated along-track floe characteristics (e.g., sea ice thickness, snow thickness, turbulent heat fluxes) for each of the unique tracks by using a weighted average of all model grid cells within 50 km of the latitude and longitude provided by LITS on that day. CICE4, the sea ice model used in the CESM-LE, uses an ice thickness distribution to represent subgrid-scale heterogeneity, which allows us to consider the predictability of concentration by thickness category. In the CESM-LE, we use five thickness categories that correspond to the following thickness ranges: 0–0.59, 0.6–1.39, 1.4–2.39, 2.4–3.59, and 3.6+ m (Hunke and Lipscomb, 2008).
For this paper, the term “seasonal” (“perennial”) corresponds to drifts from 15 October 2021 (1980) to 15 October 2022 (1981). The fundamental distinction between these regimes is the transition from old, thick, perennial sea ice to young, thin, more seasonal sea ice (Perovich, 2011). The purpose of including perennial conditions, which no longer exist in the present-day Arctic, is to contrast with the seasonal conditions in terms of how the mean state and variability, or spread in conditions, has changed over time. The specific years of model data were chosen based on model restart file availability needed to obtain daily values of all sea ice variables necessary for analysis, as well as a clear representation and contrast of perennial and seasonal conditions. To evaluate the sensitivity of our results to the start location, we also ran LITS for a range of starting locations in the Siberian Arctic within ±5∘ latitude or longitude of the given starting point for MOSAiC (85∘ N, 125∘ E). While there were small changes in the floe track locations, the results were not significantly different from those presented here and are therefore not shown.
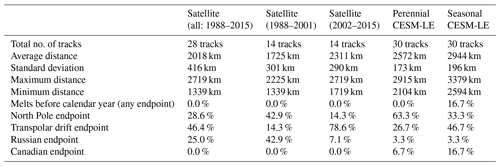
Table 1Statistics for LITS modeled tracks using satellite observations and seasonal and perennial CESM-LE conditions. The different endpoint regions (illustrated on Fig. 1) are defined with final latitude/longitude values as follows: the North Pole sector (Lat. ≥ 87∘), the Transpolar Drift sector (Lat. < 87∘, 35∘ > Long. > −60∘), the Russian sector (Lat. < 87∘, 180∘ ≥ Long. ≥ 35∘), the Canadian sector (Lat. < 87∘, 60∘ ≥ Long. ≥ −180∘).
3.1 Floe tracks
To understand whether the shift from perennial to seasonal sea ice leads to changes in floe paths, we use LITS tracks to obtain statistical information relevant to planning an expedition's year-long drift. For the satellite-derived drifts, more recent years tend to have longer drift distances (Table 1), indicating that thinner ice may lead to longer travel. While both the seasonal and perennial CESM-LE mean track distances are longer than the satellite-derived tracks (indicating that model ice speeds are faster than observations), seasonal tracks tend to travel further than perennial tracks (Table 1). Therefore, it is likely that an experiment like MOSAiC drifting in thin ice conditions will travel further than it would have when the sea ice was thicker due to observed faster drift speeds for thinner ice (Morison and Goldberg, 2012; Rampal et al., 2009; Tschudi et al., 2019). Additionally, we find that five seasonal tracks (17 %) melt before 15 October of the following year, with the earliest melt date on 29 July and the latest on 22 September. Consequently, there is an emerging risk that the floe may melt out before the end of a calendar year.
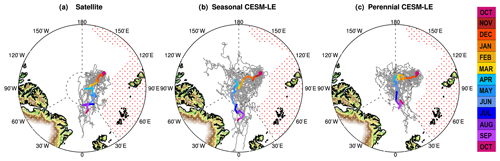
Figure 1Unique ice floe tracks (grey) for satellite observations (a), seasonal (b) and perennial (c) CESM-LE ensembles. Representative tracks (colored with corresponding months shown at far right) based on the individual tracks are overlaid. Dashed lines indicate boundaries for the Transpolar Drift, North Pole, Russian, and Canadian sectors described in Table 1. The Russian exclusive economic zone (EEZ) is shown by red stipples.
Examining individual tracks (Fig. 1, grey lines) provides perspective about paths the icebreaker might travel within a year, including high-risk paths. Figure 1 shows four different sectors in which the floe will end a year-long drift: the Russian Sector, the Canadian Sector, the Transpolar Drift sector, and the North Pole sector. Over the 1988–2015 period, the satellite-derived tracks most frequently end in the Transpolar Drift sector (46 %; 13 tracks). In the first half of the observational record, prior to 2002, many tracks end near the North Pole sector (43 %; 6 tracks) or enter the Russian sector (43 %; 6 tracks). In later years, after 2002, the satellite-derived paths tend to shift toward the Canadian sector, though most ultimately end with a Transpolar Drift path (79 %; 11 tracks). For the CESM-LE, the likely end points for tracks shift from the North Pole sector (63 %; 19 tracks) in perennial conditions to the Transpolar Drift sector (47 %; 14 tracks) in seasonal conditions. Therefore, with thinner sea ice, both the observations and model show an increased frequency of Transpolar Drift tracks. Of additional concern is the possibility that the track may enter a nation's exclusive economic zone (EEZ). In particular, if the experiment were to enter the Russian EEZ there may be an immediate cessation of all measurements, thus understanding the likelihood of this occurrence in seasonal sea ice conditions is important. Three satellite-derived tracks enter the Russian EEZ, while for the CESM-LE only one seasonal and one perennial track enter the Russian EEZ. This indicates that from this particular starting point a high-risk track into the Russian EEZ is unlikely, even with the range determined by internal variability. The CESM-LE tracks tend to have higher probability of ending in the Canadian sector, which may be related to the position of the modeled center of the Beaufort Gyre (DeRepentigny et al., 2016) that results in model tracks that tend to be shifted toward the Canadian sector.
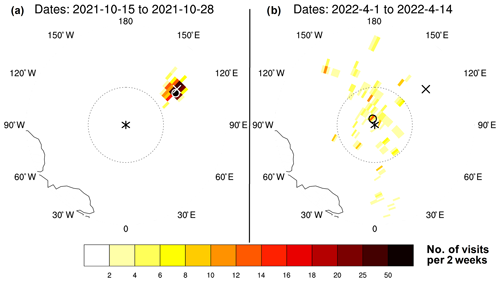
Figure 2Counts of visits to each grid cell by seasonal tracks in a 2-week period during 15–28 October (a) and 1–14 April (b). The “X” marks the starting location of the campaign, the circle marks the location of highest counts in the 2-week time period, and the star marks the North Pole. The dashed black line at 87∘ N shows, on average, where several current polar-orbiting satellites used for cryospheric research begin to lose coverage due to satellite pole holes. A satellite's pole hole is unique to its orbit inclination and instrument swath.
Figure 3Seasonal grid cell daily mean sea ice concentration (a), thickness (b), and ice age (c) on 15 October. Three random ensembles from the CESM-LE and the ensemble mean are shown. The black “X” in each map denotes the campaign starting location. The Lagrangian tracks for each ensemble member and the representative track from Fig. 1 for the ensemble mean are overlaid as black lines.
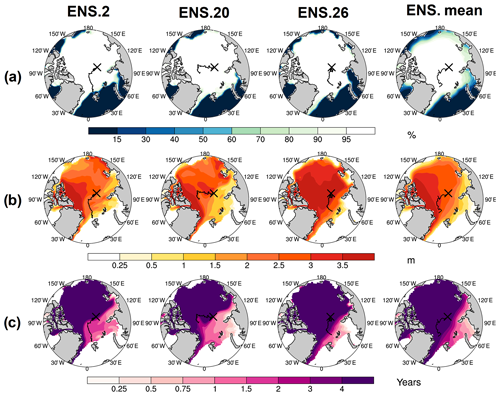
Figure 4Perennial grid cell daily mean sea ice concentration (a), thickness (b), and ice age (c) on 15 October. Three random ensembles from the CESM-LE and the ensemble mean are shown. The black “X” in each map denotes the campaign starting location. The Lagrangian tracks for each ensemble member and the representative track from Fig. 1 for the ensemble mean are overlaid as black lines.
We created maps showing the number of times each grid cell is visited by sea ice tracks over 2-week periods throughout the year (Fig. 2). These maps are also used to identify “representative” tracks (Fig. 1, colored lines) by identifying locations with high track counts that also formed a continuous path, i.e., a path in which unphysical “jumps” in the track were not permitted. It is important to note this is not a forecast of the likely path MOSAiC will take but instead is meant to represent a reasonable path given the individual tracks from ensemble members under the same climate forcing and how these may differ between seasonal and perennial conditions. While all representative tracks follow a Transpolar Drift trajectory, the representative seasonal path is longer and shifted further towards the Canadian Arctic compared to the representative observed and simulated perennial paths, which end further north (Fig. 1). The maps shown in Fig. 2 can also be used to inform the remote sensing community about the likelihood of the field experiment being observable by satellites. Tracks in close proximity to the North Pole are often not observable by most polar-orbiting satellites due to orbit inclinations and instrument swath creating gaps in coverage. These “pole holes” range in size (e.g., ∼ 82.5∘ N for CloudSat, ∼ 88∘ N for ICESat-2, and ∼ 89.3∘ N for AMSR-E) and are dependent on a satellite's orbit. Knowing when the floe is likely to be in these areas is valuable for planning and coordinating surface-based and airborne measurements to fill the high-latitude satellite “gap” (Fig. 2). Equally, knowing where and when the track is likely to emerge from satellite pole holes in spring after polar day has returned is valuable for planning visible image acquisition, such as that from DigitalGlobe's WorldView satellites (https://www.satimagingcorp.com/satellite-sensors/, last access: 10 October 2019), to support operational and scientific needs. All three representative tracks enter the satellite gap in December, but when the representative tracks exit the gap differs between September for observational and perennial tracks and July for seasonal tracks.
3.2 Seasonal floe conditions and variability
The CESM-LE also provides guidance on the range of sea ice conditions and variability that may be encountered during a year-long expedition and whether these have changed over time. Individual ensemble members provide unique realizations of equally likely sea ice states, and the ensemble mean provides guidance on the most likely conditions.
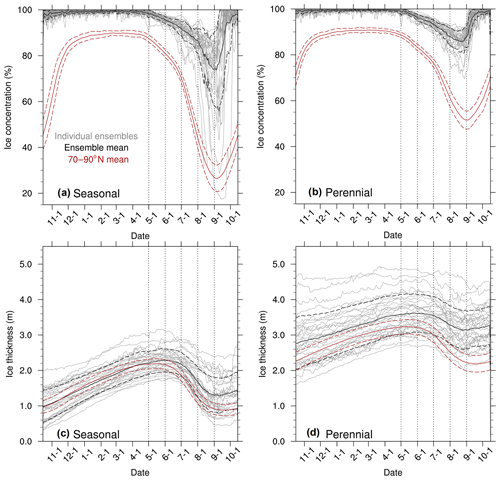
Figure 5Year-long daily mean sea ice concentration (a, b) and sea ice thickness (c, d) for seasonal tracks (left column) and perennial (right column) tracks. Ice state for each unique ice floe tracks (grey) are overlain by the ensemble mean (solid black) and polar cap (70–90∘ N) daily mean ice state (solid red) and respective ±1 standard deviation (dashed).
The initial sea ice conditions are important both logistically and scientifically. Logistically, the initial ice state has implications on the icebreaker's ability to reach the desired destination and the fuel required. Scientifically, establishing an initial location that has a mix of multiyear and first-year ice is important to ensure sampling of heterogeneous ice types. For seasonal drifts, the initial ice coverage can have a range of possible concentration configurations, but for the starting location of 85∘ N, 125∘ E, the ensemble means shows that it is likely to be within the sea ice pack (Fig. 3a), though it may be near the sea ice edge (e.g., ensemble 2). The ensemble mean initial sea ice thickness is likely to be around 0.75 m (Fig. 3b), which is within the icebreaker's limitations. The ensemble mean ice age is around 1.75 years (Fig. 3c), indicating that there are likely to be multiyear floes at this location. The variability in the initial sea ice conditions is unsurprisingly higher for seasonal conditions than for perennial conditions, which were likely to have extensive, thick (> 2 m), multiyear (> 4 year) ice at this location (Fig. 4). The increase in variability indicates that finding the ideal mix of ice conditions for MOSAiC is less certain because of the large variability in individual ensemble members sea ice states at the initiation of the campaign.
The along-track sea ice state throughout the year for each unique seasonal and perennial track provides information about the seasonal evolution and variability in sea ice concentration and thickness. The sea ice concentration for all seasonal and perennial tracks is above 95 % until about 1 May, when the concentration begins to decrease (Fig. 5a, b). For seasonal tracks, the initial ice thickness could range from 0.2 to 2 m, though it is unlikely to exceed 3 m or fall below 1 m during the year-long drift (Fig. 5c). There is a notable increase in melt season (taken here as 1 May to 15 September) ice concentration variability for seasonal conditions compared to perennial conditions. The average standard deviation for sea ice concentration is more than double for seasonal tracks (5.5 %) compared to perennial (2.6 %) tracks. In contrast, the standard deviation in sea ice thickness is higher for perennial (0.54 m) compared to seasonal (0.38 m) floes (Fig. 5d). The increased thickness variability in the perennial tracks is likely because the thick multiyear ice has a relatively weak negative ice thickness–ice growth rate feedback compared to thin ice cover. This feedback, in which thinner ice grows more rapidly because of increased heat conduction, damps ice thickness anomalies and thus the ice thickness variability (Bitz and Roe, 2004; Goosse et al., 2018). This feedback is particularly strong in a thin ice regime.
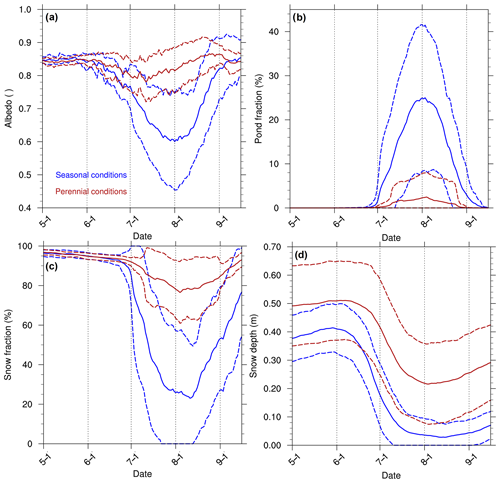
Figure 6Melt season daily along-track mean sea ice albedo (a), pond fraction of model grid cell (b), snow fraction on sea ice (c), and snow depth on sea ice (d). The ensemble mean (solid) and ±1 standard deviation envelope (dashed) are shown for seasonal (blue) and perennial (red) conditions. The melt season shown here corresponds to 1 May to 15 September.
In addition to placing observations into context, we also address the challenge of evaluating modeled sea ice using single-point observations. Compared to the Lagrangian along-track sea ice concentration, the polar cap (70–90∘ N) average concentration and variability are lower, and the change in the rate of decline occurs earlier (Fig. 5a, b). This difference is likely due to along-track positions remaining at higher latitudes (> 80∘ N), where they receive less sunlight and typically melt later than sea ice would at lower latitudes (Bliss and Anderson, 2018). Because the timing of the seasonal cycles in pan-Arctic or polar cap averages is not an accurate representation of the seasonal cycle for a given floe, future model studies comparing model output to MOSAiC observations should strive to use a Lagrangian comparison.
The variability as measured by the across-ensemble-member standard deviation is also higher for seasonal surface conditions that impact sea ice evolution – snow fraction, pond fraction, and albedo (Fig. 6). Unsurprisingly, in a warmer climate like that associated with seasonal conditions, there tends to be higher pond fraction and lower snow cover fraction. Additionally, the standard deviation for snow depth is higher for perennial (0.15 m) compared to seasonal (0.38 m) tracks because most seasonal tracks experience complete snow melt in July (Fig. 6d). In contrast, modeled perennial tracks tend not to lose all their snow, which has been previously documented in CESM simulations (Light et al., 2015). The snow differences impact the ice concentration variability through positive albedo feedback (Goosse et al., 2018; Hall, 2004; Qu and Hall, 2007), and as a result of these surface conditions the perennial tracks maintain a higher albedo throughout summer (Fig. 6a).
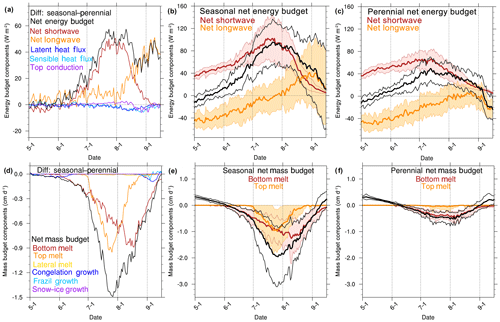
Figure 7Melt season daily along-track mean surface energy budget (a) and mass budget (d) differences (seasonal tracks minus perennial tracks). The ensemble mean (solid) and ±1 standard deviation envelope (shaded) are shown for the components with the largest differences for the energy budget (b, c) and mass budget (e, f). Components of the energy budget include net (black), net shortwave (red), net longwave (orange), latent heat flux (dark blue), sensible heat flux (light blue), and top conductive flux (purple). Components of the mass budget include net (black), bottom melt (red), top melt (orange), lateral melt (gold), congelation growth (dark blue), frazil growth (light blue), and snow–ice growth (purple). The melt season shown here corresponds to 1 May to 15 September.
There are large differences in surface conditions during the melt season between the seasonal and perennial conditions, which results in the large differences in net shortwave radiation (Fig. 7a). The variability in the seasonal energy and mass budget terms is much larger than the perennial conditions (Fig. 7b, c, e, f). Seasonal tracks have more top melt initially compared to perennial tracks, but later differences in bottom melt become dominant (Fig. 7d). For seasonal tracks the loss of snow increases surface shortwave absorption for both sea ice and the surrounding ocean, which leads to increases in top and bottom melt (Perovich et al., 2007).
These results of conditions and energy and mass budgets along the floe tracks are particularly useful for a two-way exchange of information: (1) they place context on a single year's worth of observations during a year-long field campaign; (2) remotely sensed observations along the modeled drift tracks from the year before, during, and after the MOSAiC campaign can be collected to assess the magnitude of interannual variability of the modeled variables; and (3) the observations will help constrain the range in variability shown by the model for sea ice and surface conditions.
3.3 Floe predictability
The CESM-LE also provides the opportunity to explore the initial-value predictability for the state of the expedition's sea ice floe. For campaign planning purposes, it is important when establishing an initial ice camp to be confident that the sea ice floes will be sufficiently stable to avoid endangering personnel or equipment. By calculating the autocorrelation coefficient between the 30 unique initial floe conditions and the subsequent conditions each following month throughout the year, we are able to explore how long the initial sea ice state persists. This provides information about predictability of conditions, although notably there are other factors, such as the persistence of conditions that affect the sea ice state, which can give rise to predictability and are not accounted for in the autocorrelation analysis shown here.
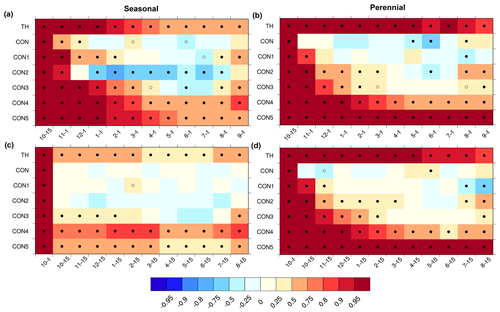
Figure 8Correlation coefficients for sea ice variables between the initial condition and conditions throughout the year for seasonal (a, c) and perennial (b, d) tracks initialized on 15 October (a, b; top row) and 1 October (c, d; bottom row). Solid (open) black dots indicate statistical significance at the 95 % (90 %) confidence level. From top to bottom, the variables shown are grid cell along-track mean ice thickness (TH), grid cell mean ice concentration (CON), and ice concentration for categories 1–5 (CON1-CON5).
For seasonal tracks with a campaign start date of October 15 there is high and significant correlation for grid cell mean sea ice thickness between the initial value and values well into the following year (Fig. 8a). While the autocorrelation is low for grid cell mean sea ice concentration, the autocorrelation for concentration of ice in thicker categories is high, which reflects the high initial-value predictability of Arctic sea ice thickness (Blanchard-Wrigglesworth et al., 2011). The negative correlations for ice in category 2 (0.6–1.39 m) are due to the nature of the ice thickness distribution and indicates that ice that is initially in this category is likely to move out of this category to thicker categories throughout the winter. The autocorrelation of sea ice variables for a seasonal floe is typically lower compared to perennial autocorrelations initialized on 15 October (Fig. 8b), suggesting lower predictability for seasonal conditions. We tested other predictors (e.g., initial fraction of open water or sea surface temperature) for the sea ice floe's state at later dates during the campaign, but these were found to have low, statistically insignificant correlations, even from the initial week and therefore were poor predictors (not shown).
The exact start date of the campaign is indefinable but may occur as early as 1 October and as late as 31 October. To understand how the predictability may change based on start date, we also evaluate the predictability characteristics for tracks initialized at the same location but on different dates. For seasonal floes, a 1 October start date results in lower autocorrelations (Fig. 8c), while a 30 October start date has nearly identical autocorrelations (not shown) compared to a 15 October start date. In contrast, for a perennial floe the autocorrelations are similar between the 1 and 15 October start dates (Fig. 8d). Because sea ice state predictors change rapidly during these 2 weeks, predictors used in perennial conditions during October may not be appropriate in seasonal conditions at the same calendar date depending at the stage of freeze-up. The evolution of differences in predictability characteristics that emerge during the autumn freeze-up are not yet well understood.
The CESM-LE is a fully coupled global climate model with well-represented Arctic sea ice mean state and variability. As an initial condition ensemble, the CESM-LE is a tool designed to explore the effects of internal climate variability and forced change. Thus, by tracking modeled sea ice floes using the CESM-LE characteristic perennial and seasonal sea ice conditions, we have an ideal framework to meet our three goals: (1) put into context a single year's observations since MOSAiC will represent a single response of the climate system to forced change, (2) provide guidance about observations that can be used to improve climate models, and (3) demonstrate how free-running climate models might assist with future campaign planning.
Substantial work by MOSAiC planners has gone into both determining a starting location (85∘ N, 125∘ E) for the campaign and developing a forecast system for the campaign once it has initialized. This study is not intended to provide a forecast for the campaign, and we leverage the likely starting location and examine the range in CESM-LE conditions to contextualize the MOSAiC campaign. As the Polarstern searches for an initial floe from which to establish camp, the CESM-LE ensemble mean indicates that there is likely to be widespread ice cover with a mix of predominantly new, thin ice and some old, thick ice, but there is wide variability in the spatial ice coverage. Starting from the assumed likely starting location, the CESM-LE indicates that in seasonal conditions a Transpolar Drift path is likely (47 %) but would not have been as likely in perennial conditions (27 %). The increase in likelihood of a Transpolar Drift path is consistent with satellite-derived tracks, which show the frequency of this type of trajectory increasing from 14 % in the first half of the satellite record to 79 % in the second half. The CESM-LE tracks show that in seasonal conditions, as compared to perennial conditions, thinner ice will drift more quickly (Morison and Goldberg, 2012; Rampal et al., 2009; Tschudi et al., 2019). The modeled Beaufort Gyre is stronger than observations due to biases in the atmospheric circulation (DeRepentigny et al., 2016), thus the modeled tracks that enter the Beaufort Gyre may be due to a combination of thin ice and particularly strong atmospheric circulation in those ensemble members. There is a small (17 %) chance the floe may melt out in August or September before a full calendar year, which was not the case for any observed or perennial floes. Future campaigns could use climate model ensembles to better understand the likely conditions contributing to outlier, hazardous paths. These simulated paths can also be used to coordinate airborne or surface measurements with acquisition of satellite imagery. We find that in a seasonal Arctic, the campaign may be visible by satellites by July, which is earlier than estimated using satellite observations or perennial conditions. Ultimately, the path that MOSAiC takes can be used to validate and improve modeled sea ice motion (e.g., Beaufort Gyre strength and location).
MOSAiC observations will focus on coupled processes, thus using a coupled climate model to analyze the representation of these coupled processes provides data that traditional weather or process modeling does not. While higher-resolution coupled regional models can also provide information on modeled coupled processes, they do not have a direct linkage to extra-polar regions present in a global climate model important for understanding the exchanges between (both into and out of) the Arctic and elsewhere. To this end, we explore how the CESM-LE results can inform data collection during MOSAiC, as well as how modelers can optimally use the data once the campaign is over to improve models. For the seasonal tracks, there is a large range in possible initial sea ice conditions, thus the campaign may start at the ice edge or well within the pack. The variability in melt season conditions is higher for the seasonal tracks than for perennial tracks, thus identifying the initial sea ice state from which the campaign will start well in advance is less certain in seasonal conditions due to the higher variability. A high-precision record in one location for one sea ice type is just one realization in the wide range of possible sea ice states, thus observations spanning a diverse range of sea ice conditions are crucial for improving modeled processes of the heterogeneous sea ice system. The initial MOSAiC camp will be established on a thick floe, which is likely to persist throughout the following year, though large variability in melt season sea ice conditions should be expected. We recommend both in situ sampling of a large range in conditions, as well as targeting airborne and spaceborne platforms on the anticipated drift tracks in the year before, during, and after the MOSAiC campaign to better understand the variability within the system. Because sea ice models represent subgrid-scale ice thickness categories and combines these into a coarser grid cell representation, it is particularly valuable to obtain observations spanning a range of ice conditions in order to enable process-oriented understanding and model representation over a fully representative distribution of sea ice conditions.
Regarding how models can best use the observational data once it is collected, we find that, when comparing modeled data to a moving, observational point-based dataset, it is optimal is to use a Lagrangian framework. This framework allows us to analyze the processes virtual floes experience, and, as they evolve in a similar way, the observations on MOSAiC will measure processes impacting the real floe's evolution in time. Compared to the Lagrangian seasonal evolution, a regional average (e.g., polar cap 70–90∘ N or pan-Arctic) has a large discrepancy in the seasonal cycle. This is mainly due to differences in solar radiation for high-latitude floes near the pole.
We also used the model to identify interesting model behavior that warrants further investigation. Using autocorrelations for the 30 unique initial floe conditions allowed us to explore how long there will be predictability in the modeled sea ice system based on the initial sea ice state. While a thick initial sea ice floe for the campaign is likely to persist well into the following year, the emergence of predictability for ice thickness or concentration during the autumn freeze-up is not well understood and was unexpected. Observations of processes occurring during the autumn freeze-up taken during MOSAiC will be beneficial for understanding the formation and evolution of the sea ice thickness distribution and how this, in turn, affects sea ice predictability throughout the year. Future modeling work could explore other predictors (e.g., SST, remote influences) on the predictability of a sea ice floe, use metrics other than autocorrelation to quantify predictability, and include perfect model experiments (e.g., Blanchard-Wrigglesworth et al., 2011; Holland et al., 2013) initialized during the freeze-up that might elucidate the mechanisms for this increase in autocorrelation.
The scripts used for this analysis in this paper can be found here: https://github.com/duvivier/MOSAIC_TC_2020 (last access: 7 April 2020, DuVivier, 2020).
The CESM-LE data are freely available from the following link: http://www.cesm.ucar.edu/projects/community-projects/LENS/ (last access: 7 April 2020, Deser and Kay, 2020; Kay et al., 2015).
AKD designed the experiments, and AKD and PD worked together to complete the Lagrangian Tracking. AKD made the figures and performed the analysis on the experiments with input from PD, MMH, and JEK. MW and DP provided particular insight about how observational data and the model analysis could be optimally used together.
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
We greatly appreciate the input of MOSAiC organizers, in particular Thomas Krumpen and Matthew Shupe, in sharing their work to determine initial conditions and providing insight about the climate model tracks. This material is based upon work supported by the National Center for Atmospheric Research, which is a major facility sponsored by the National Science Foundation (NSF) under cooperative agreement no. 1852977. The CESM project is supported primarily by NSF, and computing and data storage resources, including the Cheyenne supercomputer (https://doi.org/10.5065/D6RX99HX), were provided by the Computational and Information Systems Laboratory (CISL) at NCAR.
Alice DuVivier received support from the National Science Foundation (cooperative agreement no 1852977); Patricia DeRepentigny received support from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Council of Canada (NSERC), the Fond de recherche du Québec – Nature et Technologies (FRQNT), and the Canadian Meteorological and Oceanographic Society (CMOS) through PhD scholarships; Marika M. Holland and Donald Perovich received support from the NSF (OPP 1724748); Jennifer E. Kay recieved support from the NSF (CAREER 1554659); and Melinda Webster received support from the National Aeronautics and Space Administration’s New (Early Career) Investigator Program in Earth Science.
This paper was edited by David Schroeder and reviewed by three anonymous referees.
Alexander, M. A.: The Atmospheric Response to Realistic Arctic Sea Ice Anomalies in an AGCM during Winter, J. Clim., 17, 890–905, https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0442(2004)017<0890:TARTRA>2.0.CO;2, 2004.
Barnes, E. A. and Screen, J. A.: The impact of Arctic warming on the midlatitude jet-stream: Can it? Has it? Will it?, WIRES Clim. Change, 6, 277–286, https://doi.org/10.1002/wcc.337, 2015.
Barnhart, K. R., Miller, C. R., Overeem, I., and Kay, J. E.: Mapping the future expansion of Arctic open water, Nat. Clim. Change, 6, 280–285, https://doi.org/10.1038/nclimate2848, 2015.
Bitz, C. M. and Roe, G. H.: A Mechanism for the High Rate of Sea Ice Thinning in the Arctic Ocean, J. Clim., 17, 3623–3632, https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0442(2004)017<3623:AMFTHR>2.0.CO;2, 2004.
Blanchard-Wrigglesworth, E., Bitz, C. M., and Holland, M. M.: Influence of initial conditions and climate forcing on predicting Arctic sea ice, Geophys. Res. Lett., 38, L18503, https://doi.org/10.1029/2011GL048807, 2011.
Bliss, A. C. and Anderson, M. R.: Arctic Sea Ice Melt Onset Timing From Passive Microwave-Based and Surface Air Temperature-Based Methods, J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos., 123, 9063–9080, https://doi.org/10.1029/2018JD028676, 2018.
Boisvert, L. N. and Stroeve, J. C.: The Arctic is becoming warmer and wetter as revealed by the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder, Geophys. Res. Lett., 42, 4439–4446, https://doi.org/10.1002/2015GL063775, 2015.
Bromwich, D. H., Hines, K. M., and Bai, L.-S.: Development and testing of Polar Weather Research and Forecasting model: 2. Arctic Ocean, J. Geophys. Res., 114, D08122, https://doi.org/10.1029/2008JD010300, 2009.
DeRepentigny, P., Tremblay, L. B., Newton, R., and Pfirman, S.: Patterns of Sea Ice Retreat in the Transition to a Seasonally Ice-Free Arctic, J. Clim., 29, 6993–7008, https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-15-0733.1, 2016.
Deser, C. and Kay, J. E.: CESM Large Ensemble Community Project, available at: http://www.cesm.ucar.edu/projects/community-projects/LENS/, last access: 7 April, 2020.
Deser, C., Sun, L., Tomas, R. A., and Screen, J.: Does ocean coupling matter for the northern extratropical response to projected Arctic sea ice loss?, Geophys. Res. Lett., 43, 2149–2157, https://doi.org/10.1002/2016GL067792, 2016.
Dethloff, K., Rex, M., and Shupe, M.: Multidisciplinary drifting Observatory for the Study of Arctic Climate (MOSAiC), Geophsyical Res. Abstr., 18, EGU2016-3064, 1 pp., 2016.
DuVivier, A. K.: Analysis scripts for MOSAIC manuscript submitted to The Cryosphere, available at: https://github.com/duvivier/MOSAIC_TC_2020, last access: 7 April 2019.
Goosse, H., Kay, J. E., Armour, K. C., Bodas-Salcedo, A., Chepfer, H., Docquier, D., Jonko, A., Kushner, P. J., Lecomte, O., Massonnet, F., Park, H.-S., Pithan, F., Svensson, G., and Vancoppenolle, M.: Quantifying climate feedbacks in polar regions, Nat. Commun., 9, 1919, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-04173-0, 2018.
Hall, A.: The Role of Surface Albedo Feedback in Climate, J. Clim., 17, 1550–1568, https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0442(2004)017<1550:TROSAF>2.0.CO;2, 2004.
Holland, M. M., Blanchard-Wrigglesworth, E., Kay, J., and Vavrus, S.: Initial-value predictability of Antarctic sea ice in the Community Climate System Model 3, Geophys. Res. Lett., 40, 2121–2124, https://doi.org/10.1002/grl.50410, 2013.
Hunke, E. C. and Lipscomb, W. H.: CICE: the Los Alamos Sea Ice Model Documentation and Software Version 4.0, Los Alamos Natl. Lab. Los Alamos NM, LA-CC-06-012, 76, 2008.
IASC: MOSAiC Implementation Plan, International Arctic Science Committee, 2016.
Intrieri, J. M., Fairall, C. W., Shupe, M. D., Persson, P. O. G., Andreas, E. L., Guest, P. S., and Moritz, R. E.: An annual cycle of Arctic surface cloud forcing at SHEBA, J. Geophys. Res., 107, 8039, https://doi.org/10.1029/2000JC000439, 2002.
Jahn, A., Kay, J. E., Holland, M. M., and Hall, D. M.: How predictable is the timing of a summer ice-free Arctic?, Geophys. Res. Lett., 43, 9113–9120, https://doi.org/10.1002/2016GL070067, 2016.
Kay, J. E. and Gettelman, A.: Cloud influence on and response to seasonal Arctic sea ice loss, J. Geophys. Res., 114, D18204, https://doi.org/10.1029/2009JD011773, 2009.
Kay, J. E., Deser, C., Phillips, A., Mai, A., Hannay, C., Strand, G., Arblaster, J. M., Bates, S. C., Danabasoglu, G., Edwards, J., Holland, M., Kushner, P., Lamarque, J.-F., Lawrence, D., Lindsay, K., Middleton, A., Munoz, E., Neale, R., Oleson, K., Polvani, L., and Vertenstein, M.: The Community Earth System Model (CESM) Large Ensemble Project: A Community Resource for Studying Climate Change in the Presence of Internal Climate Variability, B. Am. Meteorol. Soc., 96, 1333–1349, https://doi.org/10.1175/BAMS-D-13-00255.1, 2015.
Klein, S. A., McCoy, R. B., Morrison, H., Ackerman, A. S., Avramov, A., de Boer, G., Chen, M., Cole, J. N. S., Del Genio, A. D., Falk, M., Foster, M. J., Fridlind, A., Golaz, J.-C., Hashino, T., Harrington, J. Y., Hoose, C., Khairoutdinov, M. F., Larson, V. E., Liu, X., Luo, Y., McFarquhar, G. M., Menon, S., Neggers, R. A. J., Park, S., Poellot, M. R., Schmidt, J. M., Sednev, I., Shipway, B. J., Shupe, M. D., Spangenberg, D. A., Sud, Y. C., Turner, D. D., Veron, D. E., Salzen, K. von, Walker, G. K., Wang, Z., Wolf, A. B., Xie, S., Xu, K.-M., Yang, F., and Zhang, G.: Intercomparison of model simulations of mixed-phase clouds observed during the ARM Mixed-Phase Arctic Cloud Experiment – I: single-layer cloud, Q. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc., 135, 979–1002, https://doi.org/10.1002/qj.416, 2009.
Krumpen, T.: Across the Arctic: What course will Polarstern follow?, available at: https://www.meereisportal.de/en/mosaic/polarstern-drift/, last access: 6 September 2019.
Krumpen, T., Belter, H. J., Boetius, A., Damm, E., Haas, C., Hendricks, S., Nicolaus, M., Nöthig, E.-M., Paul, S., Peeken, I., Ricker, R., and Stein, R.: Arctic warming interrupts the Transpolar Drift and affects long-range transport of sea ice and ice-rafted matter, Sci. Rep., 9, 5459, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-41456-y, 2019.
Kwok, R.: Arctic sea ice thickness, volume, and multiyear ice coverage: losses and coupled variability (1958–2018), Environ. Res. Lett., 13, 105005, https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/aae3ec, 2018.
Kwok, R., Cunningham, G. F., Wensnahan, M., Rigor, I., Zwally, H. J., and Yi, D.: Thinning and volume loss of the Arctic Ocean sea ice cover: 2003–2008, J. Geophys. Res.-Oceans, 114, C07005, https://doi.org/10.1029/2009JC005312, 2009.
Labe, Z., Magnusdottir, G., and Stern, H.: Variability of Arctic Sea Ice Thickness Using PIOMAS and the CESM Large Ensemble, J. Clim., 31, 3233–3247, https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-17-0436.1, 2018.
Light, B., Dickinson, S., Perovich, D. K., and Holland, M. M.: Evolution of summer Arctic sea ice albedo in CCSM4 simulations: Episodic summer snowfall and frozen summers, J. Geophys. Res.-Oceans, 120, 284–303, https://doi.org/10.1002/2014JC010149, 2015.
Lorenz, E. N.: Deterministic Nonperiodic Flow, J. Atmos. Sci., 20, 130–141, 1963.
Maslanik, J., Stroeve, J., Fowler, C., and Emery, W.: Distribution and trends in Arctic sea ice age through spring 2011, Geophys. Res. Lett., 38, L13502, https://doi.org/10.1029/2011GL047735, 2011.
Meier, W. N., Fetterer, F., Savoie, M. H., Mallory, S., Duerr, R., and Stroeve, J. C.: NOAA/NSIDC Climate Data Record of Passive Microwave Sea Ice Concentration, Version 3 [1988–2016], Natl. Snow Ice Data Cent. Boulder, CO, USA, https://doi.org/10.7265/N59P2ZTG, 2017.
Morison, J. and Goldberg, D.: A brief study of the force balance between a small iceberg, the ocean, sea ice, and atmosphere in the Weddell Sea, Cold Reg. Sci. Technol., 76–77, 69–76, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coldregions.2011.10.014, 2012.
Morrison, A., Kay, J. E., Frey, W. R., Chepfer, H., and Guzman, R.: Cloud Response to Arctic Sea Ice Loss and Implications for Future Feedbacks in the CESM1 Climate Model, J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos., 124, 1003–1020, https://doi.org/10.1029/2018JD029142, 2019.
Nghiem, S. V., Rigor, I. G., Perovich, D. K., Clemente-Colón, P., Weatherly, J. W., and Neumann, G.: Rapid reduction of Arctic perennial sea ice, Geophys. Res. Lett., 34, L19504, https://doi.org/10.1029/2007GL031138, 2007.
Perovich, D.: The Changing Arctic Sea Ice Cover, Oceanography, 24, 162–173, https://doi.org/10.5670/oceanog.2011.68, 2011.
Perovich, D. K., Light, B., Eicken, H., Jones, K. F., Runciman, K., and Nghiem, S. V.: Increasing solar heating of the Arctic Ocean and adjacent seas, 1979–2005: Attribution and role in the ice-albedo feedback, Geophys. Res. Lett., 34, L19505, https://doi.org/10.1029/2007GL031480, 2007.
Qu, X. and Hall, A.: What Controls the Strength of Snow-Albedo Feedback?, J. Clim., 20, 3971–3981, https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI4186.1, 2007.
Rampal, P., Weiss, J., and Marsan, D.: Positive trend in the mean speed and deformation rate of Arctic sea ice, 1979–2007, J. Geophys. Res., 114, C05013, https://doi.org/10.1029/2008JC005066, 2009.
Richter-Menge, J. A., Osborne, E., Druckenmiller, M., and Jeffries, M. O. (Eds.): The Arctic, in: State of the Climate in 2018, B. Am. Meteorol. Soc., 100, S141–S168, 2019.
Serreze, M. C. and Stroeve, J.: Arctic sea ice trends, variability and implications for seasonal ice forecasting, Philos. T. R. Soc. A, 373, 20140159, https://doi.org/10.1098/rsta.2014.0159, 2015.
Stammerjohn, S., Massom, R., Rind, D., and Martinson, D.: Regions of rapid sea ice change: An inter-hemispheric seasonal comparison, Geophys. Res. Lett., 39, L06501, https://doi.org/10.1029/2012GL050874, 2012.
Stroeve, J. and Notz, D.: Changing state of Arctic sea ice across all seasons, Environ. Res. Lett., 13, 103001, https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/aade56, 2018.
Swart, N. C., Fyfe, J. C., Hawkins, E., Kay, J. E., and Jahn, A.: Influence of internal variability on Arctic sea-ice trends, Nat. Clim. Change, 5, 86–89, https://doi.org/10.1038/nclimate2483, 2015.
Tschudi, M. A., Fowler, C., Maslanik, J. A., Stewart, J. S., and Meier, W. N.: Polar Pathfinder Daily 25 km EASE-Grid Sea Ice Motion Vectors, Version 3 [1988–2016], NASA Natl. Snow Ice Data Cent. Distrib. Act. Arch. Cent. Boulder, CO, USA, https://doi.org/10.5067/O57VAIT2AYYY, 2016.
Tschudi, M. A., Meier, W. N., and Stewart, J. S.: An enhancement to sea ice motion and age products, The Cryosphere Discuss., https://doi.org/10.5194/tc-2019-40, in review, 2019.
Uttal, T., Curry, J. A., Mcphee, M. G., Perovich, D. K., Moritz, R. E., Maslanik, J. A., Guest, P. S., Stern, H. L., Moore, J. A., Turenne, R., Heiberg, A., Serreze, M. C., Wylie, D. P., Persson, O. G., Paulson, C. A., Halle, C., Morison, J. H., Wheeler, P. A., Makshtas, A., Welch, H., Shupe, M. D., Intrieri, J. M., Stamnes, K., Lindsey, R. W., Pinkel, R., Pegau, W. S., Stanton, T. P., and Grenfeld, T. C.: Surface Heat Budget of the Arctic Ocean, B. Am. Meteorol. Soc., 83, 255–275, https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0477(2002)083< 0255:SHBOTA> 2.3.CO;2, 2002.





